Free Radicals, and How They Relate To Food
The best way to distinguish myself as a creative is to make my data visualizations ever more unique, and - dare I say - creative. My latest: a 3D diagram of an atomic structure. The structure? the free radical.
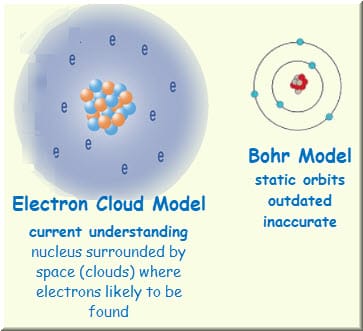
To really understand what a free radical is, its important to understand the electron cloud model, which the world adapted around the 1926. An electron cloud around an atom is where its electrons are most likely to be found, and it is distinctive because it factors in probabilities when talking about molecular shape.
The key to understanding the electron cloud model is understanding the idea of the orbital, aka a region in space where electrons are likely to be found. Basically, each 'electron cloud' is made up of a lot of different types of orbitals , each separated by a different axis plane.
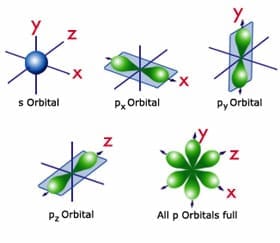
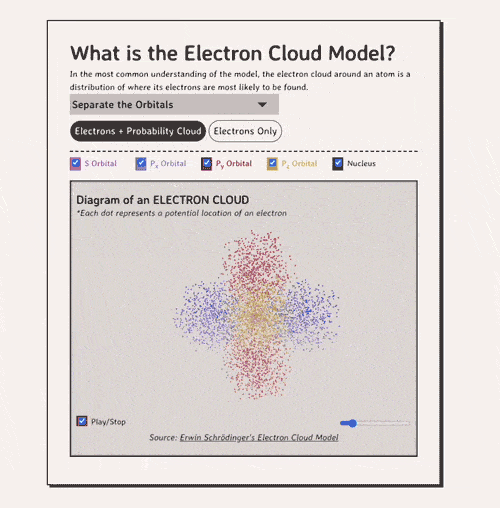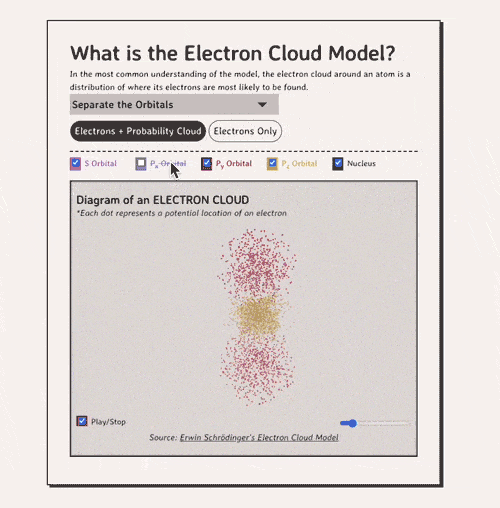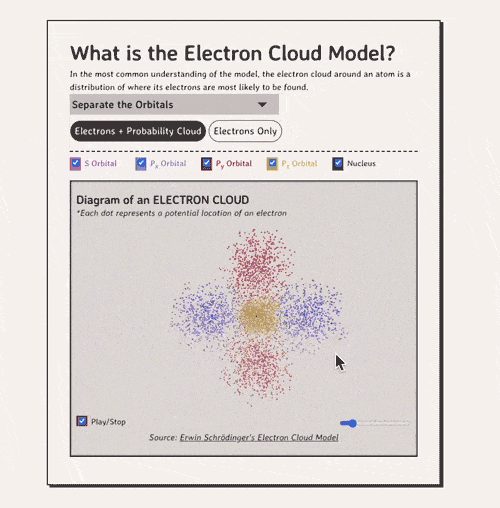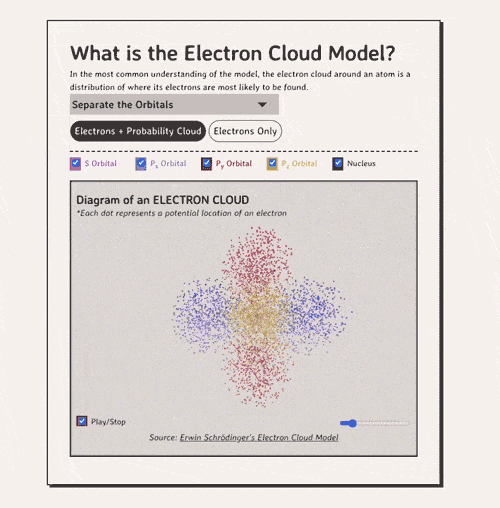
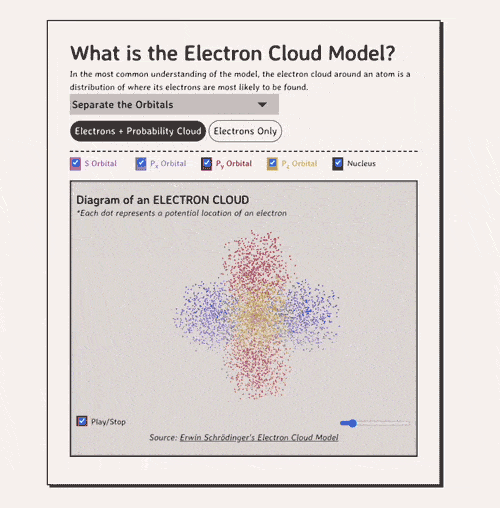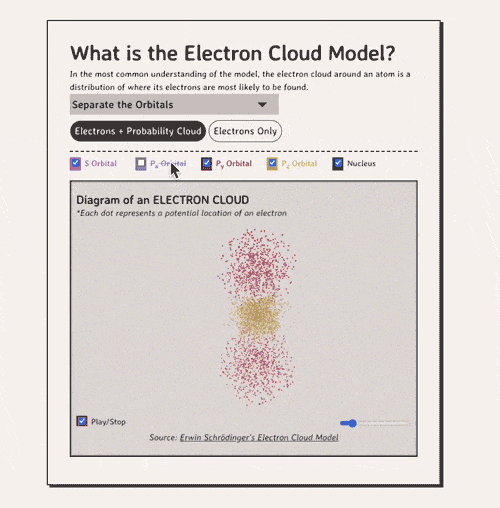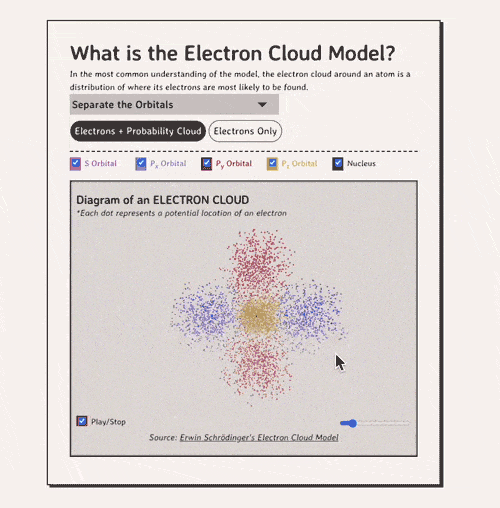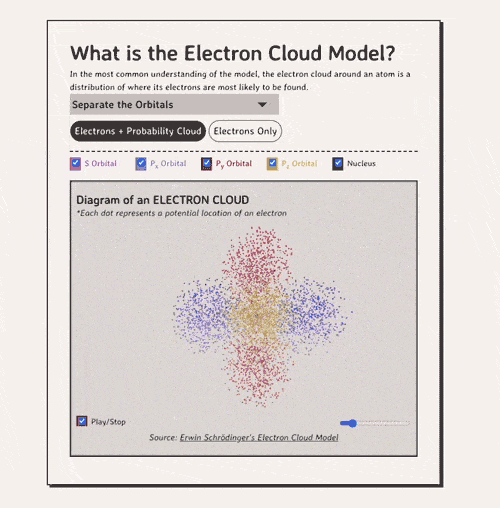
Below is my coded version of the orbitals, in three.js. I colored the orbitals different colors....the S-orbital surrounds the nucleus, while the P-orbitals - red, blue, and yellow in my diagram - make up the rest of the cloud.
What is the Electron Cloud Model?
In the most common understanding of the model, the electron cloud around an atom is a distribution of where its electrons are most likely to be found.
Diagram of an ELECTRON CLOUD
*Each dot represents a potential location of an electronNow, how do electron clouds relate to free radicals? Well, free radicals are molecules or atoms that contain one or more unpaired electrons in their outer orbital clouds. This makes free radicals highly reactive, as they try to stabilize themselves by stealing electrons from other molecules' electron clouds.
This, in turn, can cause the molecule that loses an electron to become a free radical itself, perpetuating a cycle of damage that can lead to oxidative stress in biological systems. Oxidative stress is bad for a few reasons:
- its thought to accelerate the aging process by damaging cellular components
- chronic oxidative stress can trigger and sustain inflammation
- long-term oxidative stress is linked to the development of chronic conditions such as cancer, heart disease, diabetes, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Now, stay with me. Alongside free radicals are antioxidants, which I would guess we've all heard about. Antioxidants are molecules that can donate an electron to a free radical without becoming destabilized themselves, and so, antioxidants effectively neutralize free radicals, stopping the chain reaction of molecular damage that free radicals can cause.
And thus, foods high in antioxidants are highly valued. I'm sure we've all heard about foods high in antioxidants (berries, veggies, etc), but, consider the main point of this blog to be a reminder to everyone that they are, indeed, important :)